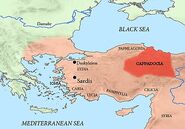
Cappadocia is a historical region in central Anatolia. It was the homeland of the Hittites, who built their capital at Hattusa, and Cappadocia was ruled by a feudal aristocracy after the Lydian king Croesus defeated the Cappadocians during the 6th century BC. The Persians later conquered Cappadocia, and it was later conquered by the Macedonian king Alexander the Great during his conquest of the Persian Empire. One of his former generals, Ariarathes, took Cappadocia after Alexander's death in 323 BC, and Persian colonists in the colony continued to practice Zoroastrianism. In 130 BC, the Cappadocians sided with the Roman Republic against the Seleucids, and their army was annihilated; in the chaos which ensued, Pontus conquered Cappadocia. In 17 AD, the Roman emperor Tiberius reduced Cappadocia to a Roman province, and it was the largest Roman province by 314 AD. Well into the Roman Empire, it continued to have a strong Persian character, and, as late as 465 AD, many Cappadocians were of Persian descent and still worshipped fire. During the 10th century, Sivas came to have a strong Armenian character due to colonization, and the Byzantine campaigns and the Seljuk invasion of Armenia led to the spread of Armenians throughout Asia Minor and the eventual creation of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia. The region was later conquered by the Ottomans, and it is still a part of modern Turkey.